U.S. Debt Burden - The Most Predictable Economic Crisis?
Interest-Rates / US Debt Oct 01, 2013 - 06:13 PM GMTBy: Axel_Merk
 Forget about a government shutdown. The quibbling over concessions to keep the government funded distracts from what might be the most predictable economic crisis. We have problems that may affect everything from the value of the U.S. dollar to investors’ savings, but also to national security.
Forget about a government shutdown. The quibbling over concessions to keep the government funded distracts from what might be the most predictable economic crisis. We have problems that may affect everything from the value of the U.S. dollar to investors’ savings, but also to national security.

In a presentation earlier this year, Erskine Bowles (of the Simpson-Bowles commission) explains why he travels around the country to drum up support for fiscal reform:
- We are doing this (traveling around the country to drum up support for fiscal reform) not for our grandkids, not even for our kids, but for us.
- If we don’t get elected officials to pull together, we face the most predictable economic crisis in history. The most predictable, but avoidable crisis.
Mr. Bowles is 68 years old; when someone his age says we need to get fiscal reform done for his generation, we should take note. The good news is that we see awareness increase. The bad news is that policy makers have an amazing ability to kick the can down the road. Former Bundesbank President Axel Weber has said policy makers choose the cost of acting versus the cost of not acting. We fully agree and would like to add that the bond market may be the one force powerful enough to get policy makers to make the tough but necessary choices. Unlike the Eurozone, however, we have a current account deficit in the U.S. which means that should the bond market apply pressure on policy makers, the U.S. dollar might come under far more pressure than the Euro has ever been.
But we are getting ahead of ourselves. To see why we have a problem, let’s look at the projections of the Congressional Budget Office (CBO); we are using their “Extended Alternative Fiscal Scenario.” The extended alternative fiscal scenario incorporates the assumptions that certain policies that have been in place for a number of years will be continued and that some provisions of law that might be difficult to sustain for a long period will be modified. From 1973-2012, government spending averaged 20.4% of GDP; in contrast government revenue averaged 17.4% of GDP. That equates to an average yearly deficit of 3%. As long as an economy grows sufficiently, it may be able to carry a sustained 3% annual deficit. A future Merk Insight might question this logic, but today’s analysis focuses on a much bigger problem.
Democrats and Republicans argue about the size of the government. Democrats tend to favor a larger government to provide healthcare or other services deemed valuable by their constituents; Republicans, in contrast, brand themselves as favoring small government. But as much as anyone may have a preference for one model or another, either approach must be financed. Financing any level of government spending can occur either through increasing revenue (taxes) or borrowing. Trouble is that there aren’t enough rich folks out there to tax to mend the system. Consider the following projection by the CBO:
- In 10 years, our annual budget deficit is projected to be 4.5% of GDP.
- In 25 years, our annual budget deficit is projected to be 13.6% of GDP.
- In 35 years, our annual budget deficit is projected to be 18.7% of GDP.
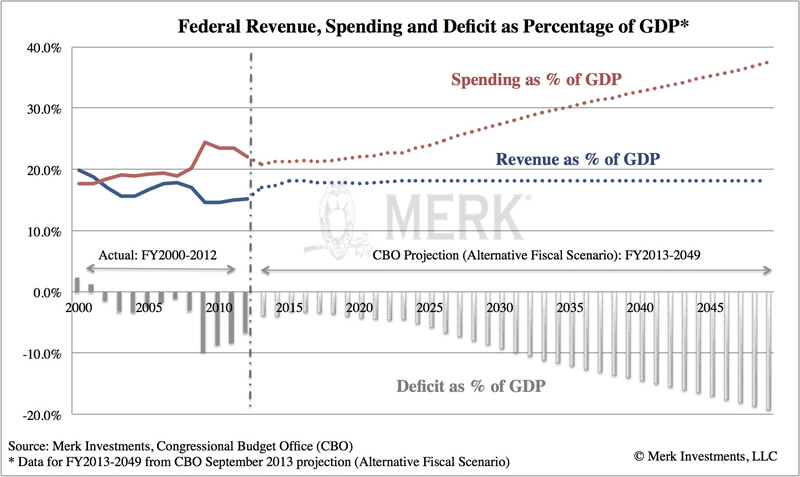
You might shrug off these numbers as unrealistic given that it’s impossible to forecast 35 years out. However, keep in mind that the biggest driver of expenses in the coming 35 years are known as “entitlements,” taking Social Security, Medicare & Medicaid together, these expenses are expected to rise from 9.3% to 15.7% of GDP; that’s an increase of 6.4% of GDP. If one accepts a substantially larger tax burden, possibly by introducing a national sales tax or carbon tax, one could conceivably finance this increase, although getting the political majority for such taxes might be elusive.
But the biggest elephant in the room is interest expense. As we keep piling on deficits at some point the cost of borrowing might increase to rates that are more in line with historic averages, and we have a problem:
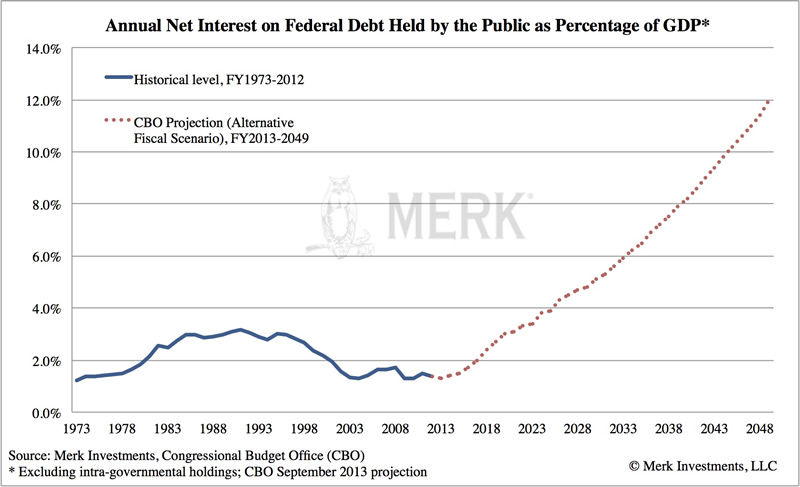
According to the CBO, in 2048, we will be spending almost 12% of GDP on interest expense, compared to just over 1% now. Differently said, as a share of GDP, we will be paying more in 2048 for entitlements and interest expense than we currently pay for all government services combined. Said still another way, even with substantially higher taxes, there may not be any money to pay for the military, education, or infrastructure. In fact, Republicans and Democrats can stop arguing about discretionary spending, as there might not be any to fight over! Mr. Bowles argues, and we agree, that our deficits might be the biggest threat to our national security.
Now there’s a thing or two we can learn from Europe. Most notably that policy makers can be incredibly creative when it comes to kicking the can down the road. Culturally, there are differences, too. In Germany, austerity sells. In the U.S., we may be much more tempted to count on the Federal Reserve to help us finance our deficits.
In this context, we think the biggest threat we are facing might be economic growth. That’s because economic growth may send the bond market down, increasing the cost of borrowing. The U.S. currently pays just under 2% on its marketable debt; in 2001, it was over 6%. We are not suggesting that the average cost of borrowing will shoot up overnight. But let’s look at just the next 10 years. The below chart shows a CBO projection next to a projection that suggests we revert to a slightly higher rate, namely the rate that was the average for the past 40 years. Unrealistic? You judge. But it suggests that we might be paying $1.2 trillion in interest expense in 2023:
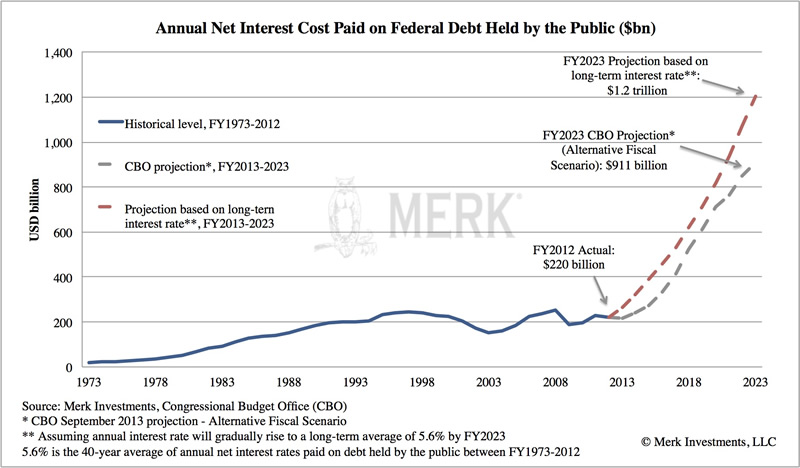
As indicated, with the exception of our suggestion that interest rates might move back up to their historic average, the estimates are CBO projections. If there were another military conflict, for example, expenses could easily be higher.
So what does it mean for investors? The most obvious choice might be to consider shorting bonds. But while we agree that bonds may be one of the worst investments over the coming decades, be warned that it can be very expensive to short bonds. Markets tend to exert maximum pain on investors; as such, it’s conceivable that bonds hold on much longer than one might think, possibly even rise. During this “wait and see” period, investors shorting bonds have to pay the interest on them.
A more effective way to prepare for what lies ahead might be to focus on the greenback. As indicated earlier, the U.S. has a current account deficit. That means foreigners have to buy U.S. dollar denominated assets to keep the dollar from falling to cover the deficits. Higher interest rates might attract investors, but if one believes the Federal Reserve might keep rates artificially low, it also means that Treasury securities would be intentionally overpriced. Less abstractly speaking, if you think the Bank of Japan in Japan or the Fed in the U.S. might try to keep a lid on yields, the currency may well be the valve. In fact, we would go as far as to argue that we cannot afford high positive real interest rates. As a result, the Fed might need to err on the side of inflation rather than cripple the economy. Sure, a hawkish Fed might be able to hike rates in the short-term, but let the economy kick into higher gear. If we look at what happened, for example, in Spain, perception maters more than reality: Spain had very prudent debt management, with an average duration of about 7 years; yet the market started to lose confidence, causing concern in the market that Spain might lose access to the market. Similarly, in the U.S., the numbers above matter little should investors lose confidence. By all means, U.S. markets are deeper and more liquid than Spanish markets. But to us, it also suggests that policy makers will be more tempted to kick the can down the road, only exacerbating the day of reckoning.
All the more so, shorting bonds may only be for the brave. Diversifying out of the greenback, however, be that through gold or a basket of currencies, is also risky, but allows investors to potentially take advantage of other opportunities along the way. A more active investor may want to contemplate whether there’s money to be made from the “currency wars” that might rage as different regions of the world address their challenges in different ways. None of these are easy choices, but doing nothing may also be a risky proposition, as the purchasing power of the dollar may increasingly be at risk.
Please register to join us for an upcoming Webinar as we dive into these dynamics in more detail. Also make sure you subscribe to our newsletter so you know when the next Merk Insight becomes available.
Manager of the Merk Hard, Asian and Absolute Return Currency Funds, www.merkfunds.com
Rick Reece is a Financial Analyst at Merk Investments and a member of the portfolio management
Axel Merk, President & CIO of Merk Investments, LLC, is an expert on hard money, macro trends and international investing. He is considered an authority on currencies. Axel Merk wrote the book on Sustainable Wealth; order your copy today.
The Merk Absolute Return Currency Fund seeks to generate positive absolute returns by investing in currencies. The Fund is a pure-play on currencies, aiming to profit regardless of the direction of the U.S. dollar or traditional asset classes.
The Merk Asian Currency Fund seeks to profit from a rise in Asian currencies versus the U.S. dollar. The Fund typically invests in a basket of Asian currencies that may include, but are not limited to, the currencies of China, Hong Kong, Japan, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan and Thailand.
The Merk Hard Currency Fund seeks to profit from a rise in hard currencies versus the U.S. dollar. Hard currencies are currencies backed by sound monetary policy; sound monetary policy focuses on price stability.
The Funds may be appropriate for you if you are pursuing a long-term goal with a currency component to your portfolio; are willing to tolerate the risks associated with investments in foreign currencies; or are looking for a way to potentially mitigate downside risk in or profit from a secular bear market. For more information on the Funds and to download a prospectus, please visit www.merkfunds.com.
Investors should consider the investment objectives, risks and charges and expenses of the Merk Funds carefully before investing. This and other information is in the prospectus, a copy of which may be obtained by visiting the Funds' website at www.merkfunds.com or calling 866-MERK FUND. Please read the prospectus carefully before you invest.
The Funds primarily invest in foreign currencies and as such, changes in currency exchange rates will affect the value of what the Funds own and the price of the Funds' shares. Investing in foreign instruments bears a greater risk than investing in domestic instruments for reasons such as volatility of currency exchange rates and, in some cases, limited geographic focus, political and economic instability, and relatively illiquid markets. The Funds are subject to interest rate risk which is the risk that debt securities in the Funds' portfolio will decline in value because of increases in market interest rates. The Funds may also invest in derivative securities which can be volatile and involve various types and degrees of risk. As a non-diversified fund, the Merk Hard Currency Fund will be subject to more investment risk and potential for volatility than a diversified fund because its portfolio may, at times, focus on a limited number of issuers. For a more complete discussion of these and other Fund risks please refer to the Funds' prospectuses.
This report was prepared by Merk Investments LLC, and reflects the current opinion of the authors. It is based upon sources and data believed to be accurate and reliable. Opinions and forward-looking statements expressed are subject to change without notice. This information does not constitute investment advice. Foreside Fund Services, LLC, distributor.
Axel Merk Archive |
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



