Western Economies Hit by Dual Shocks of Rising Commodity Prices and Financial Market Credit Crisis
Interest-Rates / Inflation Nov 28, 2007 - 02:31 PM GMTBy: Adrian_Ash
 "...You can either bail out the big banks with a flood of cheap money, or you can keep a lid on inflation. You can't do both, not according to history. And sometimes – like now – you'll be hard put to achieve either..."
"...You can either bail out the big banks with a flood of cheap money, or you can keep a lid on inflation. You can't do both, not according to history. And sometimes – like now – you'll be hard put to achieve either..."
"THE ECONOMY has been hit by two shocks," said Andrew Sentance, a Bank of England policymaker, in a speech on Tuesday night.
He was talking specifically about the British economy, but these two shocks have smacked policy-wonks square in the face across the developed world.
The two ugly fists – both with "HATE" tattooed on the knuckles – are "financial market turbulence and a sharp rise in oil and some other commodity prices."
"[They] are operating in opposing directions in terms of their impact on inflation," says the Bank of England's man. "So judging the appropriate monetary policy response will not be easy."
But who needs to judge the right response when you've got a printing press and an unlimited line of credit from tax-payers?
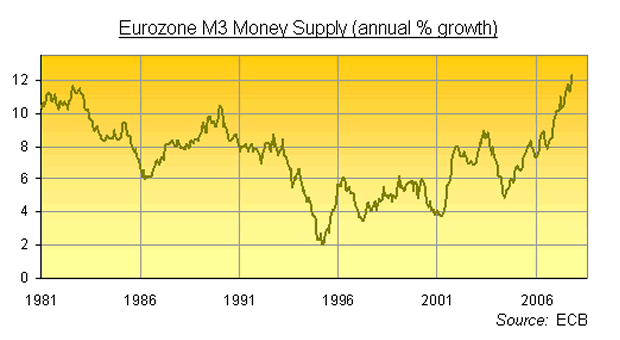
Growth in the European money supply hit a 28-year record in October, the central bank reported today (Weds).
The broad M3 money supply – "which the ECB uses as a gauge of future inflation," as Bloomberg notes – rose 12.3% from Oct. last year, the fastest rate of growth since July 1979. But this monetary inflation can only rise faster when November's numbers come out late in Dec.
Last week alone, the European Central Bank promised to supply the money markets with an extra €30 billion ($44.27bn) in short-term funds, "another indication that the credit crisis is far from over," as Sean O'Grady reports for The Independent in London,
So far, however, no cigar. On Wednesday this week, the ECB made its biggest loan of three-month money since April 2001, as the global credit crunch pushed the interbank lending rate up to 4.743%.
The ECB's current target rate for Eurozone interest rates is 4.0%, and these short-term loans are designed to help ease upward pressure on the free-market rate by making easy with central-bank cash.
But even after Wednesday's record auction of €50 billion ($73.7bn) "we didn't see any effect on markets," one money-market trader told Reuters.
"The amount [that private banks are] needing is a lot more than the ECB is allotting."
Resolving tensions in the financial markets is only one-half of a central banker's task, however. His other key responsibility – and central bankers are almost without fail always male, if not men – is defending "price stability". In other words, inflation must not be allowed to rise above some target or other, decided over tea and biscuits in the hushed conference suites where politicians and central bank wonks chew the cud.
The inflation target is currently set at 2% in both Europe and the United Kingdom . On Tuesday this week, however, the Federal Statistics Office of Germany announced that consumer-price inflation in the world's third-largest economy will rise by 3.0% in Nov. –the highest rate of price increases since Feb. 1994.
"A sense of impending inflation is currently influencing German consumers," warns the highly-regarded GfK consultancy. "The positive factors currently evident, such as the sustained improvement on the job market and rising incomes, seem unable to prevent the evaporation of optimism."
"Solid anchoring of inflation expectations is all the more important in a period of turbulences associated with this market correction," as Jean-Claude Trichet, president of the European Central Bank, said in a speech on Monday this week.
That neatly sums up the head-scratcher now costing central bankers their hair the world over. You either bail out the money markets with a flood of liquidity...or you keep a lid on inflation.
You can't do both, not according to history. And every so often – not least when you're bruised and beaten by a fearful credit crunch on one side and a hateful oil-price shock on the other – it seems you can't achieve either.
Just ask Andrew Sentance at the Bank of England. In Tuesday night's speech, he 'fessed up to an inflationary mess that looks a little like this...
The US Federal Reserve, meantime, is also presumed to be targeting 2% annual growth in its Consumer Prices.
But just like the ECB too, it's also pumping money into the New York credit market at a record clip.
Can central bankers really have it both ways?
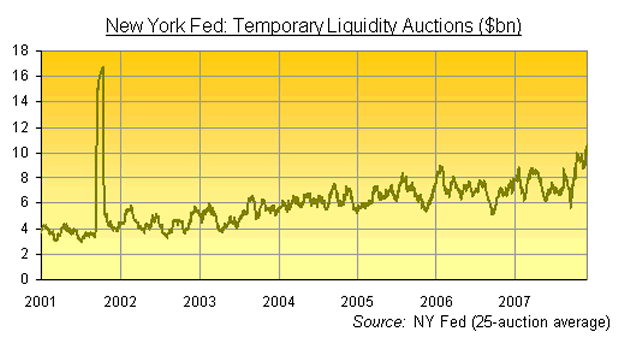
The US Fed is forever making short-term loans to the money markets. Adding liquidity is nothing unusual.
The Fed offers money to the big New York banks in exchange for good-quality securities – securities such as, say, US Treasury bonds or government agency debt. And it will lend money for anything between one day and two weeks or more.
On any one day, you might find the New York Fed making two, three or more of these loans via auction. And between the start of 2001 and the end of last month, the average sum lent in each of these auctions was $6.01 billion.
Since the start of this month, in contrast, each of the Fed's short-term liquidity auctions has averaged $10.17 billion.
But let's put quantity to one side for a moment, even if it does seem to be driving a sharp rise in German consumer-price inflation. The quality of the collateral that the Fed is accepting when it makes these loans has changed dramatically, too.
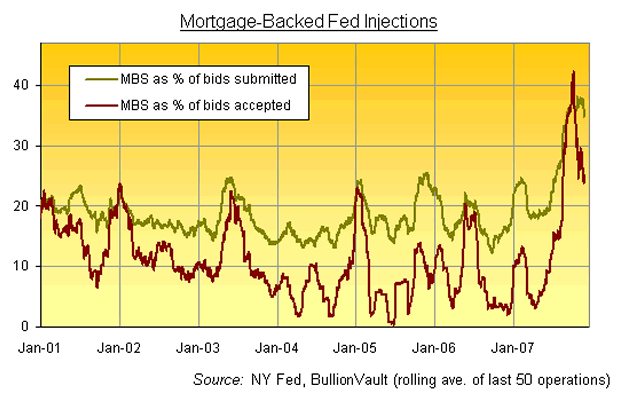
The Fed has always been happy to accept mortgage-backed bonds as security for the short-term cash injections it makes.
If the New York interbank lending rate needs a little shot in the arm to cool it down, AAA-rated mortgage-backed securities are just fine. But as you can see, the big banks stepping up to the Fed's auctions have always been keen to use more mortgage-backed securities (MBS) as collateral than the Fed would accept.
Indeed, the ratio of MBS submitted to MBS accepted averaged only 0.55 between Nov. 2000 and the end of July '07. More times than not, the Fed said "no" to home-loan backed bonds and demanded US Treasury notes or agency debt as collateral instead.
Since the credit crunch first bit at the start of August, however, the New York Fed has relented somewhat. The ratio of MBS submitted to MBS accepted when bidding for the Fed's cash has risen to 0.85.
And while the size of the Fed's injections – as well as the volume of mortgage-backed bonds held against them – have both grown substantially, the frequency of those injections has also soared. There were 29 temporary Fed injections in the first 28 days of November alone.
Over the preceding seven years, the New York Fed averaged fewer than 25 injections per calendar month.
But it's not only the Fed that's supporting the local housing market by accepting mortgage-backed bonds as collateral for new loans. Last week, Australia 's central bank lent A$500 million – some US$435m – in a series of re-purchase agreements based on mortgage-backed bonds. On Thursday alone it bought A$100 million of home-loan debt, set to mature in just over three months.
"This is the first high-volume activity ever in this market and may encourage further investor participation," reckons Warren Mellor, an analyst at National Australia Bank in Sydney , talking to Bloomberg. It might just encourage Australia 's financial firms to park as much of their home-loan inventory at the Reserve Bank, too.
Sales of Australian mortgage-backed bonds sank by 94% between July and Sept., the newswire adds, down to a meager A$1.8 billion – a five-year low.
Can the Reserve Bank reverse this slump? It claims to love mortgage-backed bonds so much right now, it's willing to lend hard cash against them at a bargain rate of interest.
Sydney's interbank lending rate for 3-month loans ended last week at 7.165%, just shy of an 11-year high. The RBA, however, was happy to lend for 0.24% below that market rate.
Or put another way, the flood of money trying to wash away the current slump in world credit markets is truly global.
Think this will help ease inflation in your cost of living?
By Adrian Ash
BullionVault.com
Gold price chart, no delay | Free Report: 5 Myths of the Gold Market
City correspondent for The Daily Reckoning in London and a regular contributor to MoneyWeek magazine, Adrian Ash is the editor of Gold News and head of research at www.BullionVault.com , giving you direct access to investment gold, vaulted in Zurich , on $3 spreads and 0.8% dealing fees.
(c) BullionVault 2007
Please Note: This article is to inform your thinking, not lead it. Only you can decide the best place for your money, and any decision you make will put your money at risk. Information or data included here may have already been overtaken by events – and must be verified elsewhere – should you choose to act on it.
Adrian Ash Archive |
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



